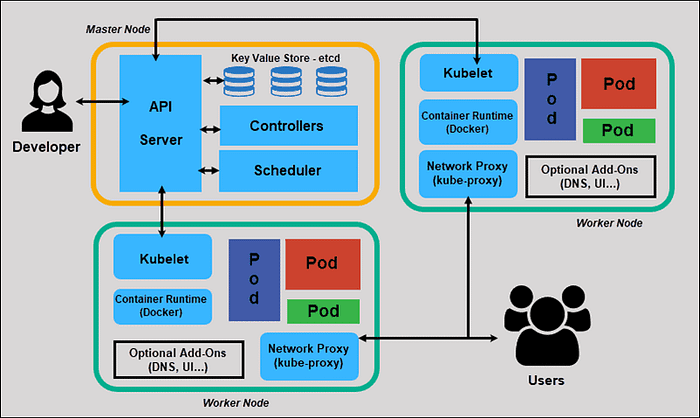
The architecture of a Kubernetes (K8s) system is composed of several components that work together to manage and orchestrate containerized applications. The main components of a K8s architecture include:
- etcd: A distributed key-value store that stores the configuration data of the cluster. It is used to store the configuration data of the cluster and its current state. It allows the master and worker nodes to maintain a consistent view of the cluster state.
- API Server: The component that exposes the Kubernetes API and handles communication with the other components. The API server is the main entry point for interacting with the cluster and it is responsible for handling all the RESTful operations that are used to interact with the cluster.
- Controller Manager: A component that manages the state of the cluster and ensures that the desired state is achieved. The controller manager watches the state of the cluster and makes decisions on how to move the cluster to the desired state. Some examples of controllers are the Replication Controller, Deployment and StatefulSet.
- Scheduler: A component that schedules pods to run on worker nodes. The scheduler is responsible for determining which worker node to run a pod on, based on a set of predefined rules and resource availability.
These components work together to provide an unified and consistent view of the state of the cluster, and to ensure that the desired state of the cluster is achieved. For example, the API server communicates with the etcd to retrieve the desired state of the cluster, and the controller manager communicates with the API server to update the state of the cluster.
It is important to note that etcd should be highly available, as it stores the state of the cluster. And the master nodes should also be highly available, as they are the control plane of the cluster and the communication point between the worker nodes and the user.
The worker node in a Kubernetes (K8s) cluster is responsible for running the containerized workloads. The main components of a worker node include:
- Kubelet: A component that communicates with the master node and manages the containers running on the node. The kubelet is responsible for ensuring that the containers are running as expected, and it communicates with the master node to report the state of the node and the containers running on it.
- Container Runtime: This is the component that is responsible for running the containers, such as Docker or containerd. This component is responsible for creating, starting, stopping, and deleting the containers on the worker node.
- Pod: A pod is the smallest and simplest unit in the Kubernetes object model that can contain one or more containers. Pods provide a logical host for one or more containers, and they are the basic unit of deployment in K8s.
- Kube-proxy: a component that runs on each worker node and is responsible for handling network communication for pods running on the node.
- Volume: Kubernetes Volumes are used to provide persistent storage for pods, and they can be backed by various types of storage, such as local storage, NFS, or cloud-based storage.

1 Comment
May 6, 2023
The design is simple and elegant. The customer support on this product is also amazing. I would highly recommend you to purchase templates from the Marketify team! Thank you for the wonderful project.